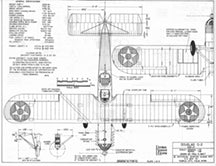
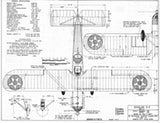
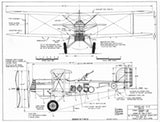
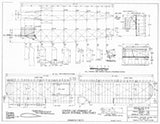
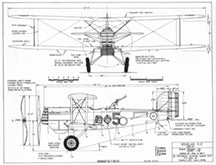
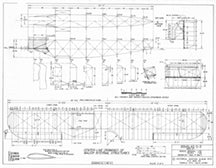
Drawing - Paul Matt - Douglas O-2
$ 1.49
Brand Kiona Publishing, Inc.
The Douglas O-2 was a 1920s American observation aircraft built by the Douglas Aircraft Company.
The Douglas O-2 was a conventional but reliable biplane, which attracted orders for 25 more aircraft: 18 O-2A equipped for night flying and six O-2B dual-control command aircraft for the US Army. Plus, there was one civil O-2BS modified for James McKee, who made a trans-Canada flight in September 1926. In 1927 the O-2BS was adapted as a three-seater with a radial engine.
The O-2Hs were an entirely new design but continued the same basic model number. Major differences were heavily staggered wings, a more compact engine installation, and clean landing gear secured to the fuselage.
Up to 2011 there were no O-2's known to exist. However, in 2011 the wreckage of O-2H 29-163 that crashed out of Kelly Field Texas on March 16, 1933 has been positively identified. The only similar aircraft to exist is a restored Douglas M-2 mailplane and a follow-on derivative of the O-25 variant, an O-38.
Specifications:
- Crew: 2
- Length: 30 ft 0 in (9.14 m)
- Wingspan: 40 ft 10 in (12.45 m)
- Height: 10 ft 0 in (3.05 m)
- Wing area: 362 ft2 (33.6 m2)
- Airfoil: Clark Y
- Empty weight: 2,857 lb (1,296 kg)
- Gross weight: 4,484 lb (2,034 kg)
- Max takeoff weight: 4,550 lb (2,064 kg)
- Fuel capacity: 110 US gal (92 imp gal; 420 l) in a single fuselage tank ahead of and below the pilot's cockpit
- Powerplant: 1 × Liberty V-1650-1 V-12 liquid-cooled piston engine, 435 hp (324 kW)
- Propellers: 2-bladed metal propeller
- Performance
- Maximum speed: 134.5 mph (216.5 km/h, 116.9 kn) at sea level
- Cruise speed: 110 mph (180 km/h, 96 kn)
- Range: 512 mi (824 km, 445 nmi)
- Service ceiling: 16,900 ft (5,200 m)
- Rate of climb: 1,075 ft/min (5.46 m/s)
- Wing loading: 12.4 lb/ft2 (61 kg/m2)
- Power/mass: 0.0971 hp/lb (0.1596 kW/kg)
* All downloadable drawings and photos are high resolution — 300 dpi